
Understanding your Database Instance in RDS
After we create an instance in AWS RDS, the new instance will showing in the Databases list. From this list, we can see the name, rule, size, status and CPU size and so on.
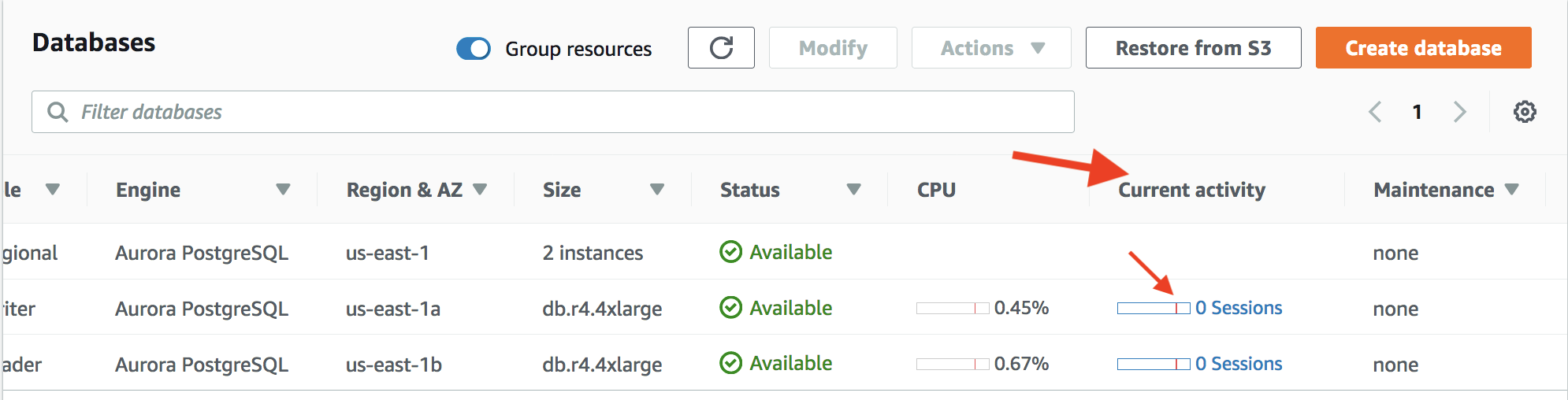
Current activity
There is a very important column named Current activity, it will refresh every seconds automatically. It shows that currently how many CPUs are using.
Sessions means Average Active Sessions (AAS for short).
There is a red vertical line on the bar, it tells if current active sessions are exceeding or not. The Max CPU value is determined by the number of vCPU (virtual CPU) cores for your DB instance.
vCPU
vCPU is short for Vitual CPU. For example, you have an RDS instance with the value of vCPU 16, that means your can have 16 cocurrent threads to process the task.
If your logic is very sample, for example 10 insertions per seconds, normally each moment one CPU is enougth to process the task. The value of Sessions should be a decimal value less that 1.
A 16-vCPU instance can handle about 200K per second inserting, that means at this situation, the system will use all the vitual CPU to process the task. And you can see the value of Sessions will became to 16 nearly.
But if you have a higher rate of data to handle, the value of Sessions will become a number greater that 16. For example 18, at this situation, the bar will become red and your task will become slow, this means 16 cocurrent threads are not enough to handle all the tasks, there are 2 tasks must be wait for other tasks to finish.
References
- https://dba.stackexchange.com/a/71304
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/USER_PerfInsights.html
- https://www.slideshare.net/AmazonWebServices/using-performance-insights-to-optimize-database-performance-dat402-aws-reinvent-2018
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/instance-optimize-cpu.html
- https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/physicalcores/